24 Hour Emergency
Open 24/7 for convenience, quick and easy access
Call us
+998 99 017-36-825/1 Building, 1 District, Chilanzar District
Tashkent, UzbekistanMon-Fri: 09:00-18:00: Sat: 09:00-15:00.
info@gmed.uz


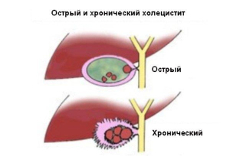
Chronic cholecystitis is the most common chronic disease affecting the biliary tract and gallbladder. Inflammation affects the walls of the gallbladder, in which stones sometimes form, and motor-tonic disorders of the biliary (biliary) system occur.
Currently, 10-20% of the adult population suffers from cholecystitis, and this disease has a tendency to further increase.
This is due to a sedentary lifestyle, the nature of nutrition (excessive consumption of food rich in animal fats - fatty meat, eggs, butter), an increase in endocrine disorders (obesity, diabetes mellitus). Women get sick 4 times more often than men, this is due to the use of oral contraceptives, pregnancy.
Chronic non-calculous cholecystitis
Inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder, in which calculi (stones) are not found in its lumen and ducts, is called acalculous cholecystitis.
Non-calculous (calculous) chronic cholecystitis, as a rule, is a consequence of conditionally pathogenic microflora. It can be caused by Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, somewhat less often Proteus, Enterococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
In some cases, there are non-calculous cholecystitis, which are caused by pathogenic microflora (typhoid bacilli, shigella), protozoal and viral infection. Microbes can enter the gallbladder through the blood (hematogenous route), through the lymph (lymphogenous route), from the intestine (by contact).
Causes
Why does chronic cholecystitis occur, and what is it? The disease may appear after acute cholecystitis, but more often develops independently and gradually. In the occurrence of the chronic form, various infections are of the greatest importance, in particular E. coli, typhoid and paratyphoid bacilli, streptococci, staphylococci and enterococci.
Primary sources of infection can be:
acute or chronic inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract (infectious enterocolitis - inflammatory bowel disease, pancreatitis, appendicitis, intestinal dysbacteriosis),
respiratory tract (sinusitis, tonsillitis), oral cavity (periodontal disease),
inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis),
reproductive system (adnexitis - in women, prostatitis - in men),
viral liver disease,
parasitic invasion of the biliary tract (giardiasis, ascariasis).
Cholecystitis always begins with disturbances in the outflow of bile. It stagnates, in connection with this, cholelithiasis, JVP, which are the immediate precursors of chronic cholecystitis, can develop. But there is also a reverse movement of this process. Due to chronic cholecystitis, pancreatic motility slows down, bile stasis develops, and stone formation increases.
Symptoms of chronic cholecystitis
When chronic cholecystitis occurs, the main symptom is pain symptoms. Adults feel dull aching pain in the right hypochondrium, which usually occurs 1-3 hours after taking plentiful, especially fatty foods and fried foods.
The pains radiate to the top, to the region of the right shoulder, neck, scapula, sometimes to the left hypochondrium. It is aggravated by physical exertion, shaking, after taking spicy snacks, wine and beer. When cholecystitis is combined with cholelithiasis, sharp pains similar to biliary colic may appear.
Along with pain, dyspeptic symptoms occur: a feeling of bitterness and a metallic taste in the mouth, belching with air, nausea, bloating, alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Risk factors
There are various forms of predisposition to the disease associated with the individual characteristics of a person, primary pathologies, nutrition and heredity. Doctors must take into account the presence of risk factors for cholecystitis during examinations.
Key risk factors:
- Obesity and significant weight loss within a few months.
- Taking certain medications. In particular, the risk of developing inflammation in the gallbladder increases with the use of hormonal drugs.
- Pregnancy.
- Chronic diseases of the intestines, liver and pancreas.
- Surgical treatment of abdominal organs, injuries.
- Chronic foci of inflammation in different parts of the body.
- Prolonged parenteral nutrition.
- Improper diet or prolonged fasting.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages.
- Myocardial infarction and other heart diseases.
- Vascular disorders in diabetes mellitus.
- Abnormal reflux of pancreatic secretions into the gallbladder (pancreatobiliary reflux).
- Insufficient physical activity.
Chronic cholecystitis does not occur suddenly, it develops over a long period of time, and after exacerbations, against the background of treatment and diet, periods of remission occur, the more carefully the diet and maintenance therapy are followed, the longer the period of absence of symptoms.
You can safely start treatment, which we carry out as quickly and efficiently as possible in Tashkent. Gatling Med Clinic will make you feel confident in yourself and in your health!
Open 24/7 for convenience, quick and easy access
Qualified and certified doctors for quality healthcare
Cost effective, comprehensive and clinical laboratory services
